Scatter plot with regression line. As we said in the introduction, the main use of scatterplots in R is to check the relation between variables.For that purpose you can add regression lines (or add curves in case of non-linear estimates) with the lines function, that allows you to customize the line width with the lwd argument or the line type with the lty argument, among other arguments. Time Series Plot From Long Data Format: Multiple Time Series in Same Dataframe Column. In this example, I construct the ggplot from a long data format. That means, the column names and respective values of all the columns are stacked in just 2 variables (variable and value respectively). We can pass in additional parameters to control the way our plot looks. You can read about them in the help section?hist. Some of the frequently used ones are, main to give the title, xlab and ylab to provide labels for the axes, xlim and ylim to provide range of the axes, col to define color etc. Additionally, with the argument freq=FALSE we can get the probability distribution instead of.
An effective and accurate data visualization is an important part of a statistical analysis. It can make your data come to life and convey your message in a powerful way.
R has very strong graphics capabilities that can help you visualize your data.
The plot() function
In R, the base graphics function to create a plot is the plot() function. It has many options and arguments to control many things, such as the plot type, labels, titles and colors.

Syntax
The syntax for the plot() function is:
plot(x,y,type,main,xlab,ylab,pch,col,las,bty,bg,cex,…)
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
| x | The coordinates of points in the plot |
| y | The y coordinates of points in the plot |
| type | The type of plot to be drawn |
| main | An overall title for the plot |
| xlab | The label for the x axis |
| ylab | The label for the y axis |
| pch | The shape of points |
| col | The foreground color of symbols as well as lines |
| las | The axes label style |
| bty | The type of box round the plot area |
| bg | The background color of symbols (only 21 through 25) |
| cex | The amount of scaling plotting text and symbols |
| … | Other graphical parameters |
Create a Simple Plot
To get started with plot, you need a set of data to work with.
Let’s consider the built-in pressure dataset as an example dataset. It contains observations of the vapor pressure of mercury over a range of temperatures.
To create a plot just specify the dataset in plot() function.

Change the Shape and Size of the Points
You can use the pch (plotting character) argument to specify symbols to use when plotting points.
Here’s a list of symbols you can use.
For symbols 21 through 25, you can specify border color using col argument and fill color using bg argument.
To alter the size of the plotted characters, use cex (character expansion) argument.
Changing the Color
You can change the foreground color of symbols using the argument col.
R has a number of predefined colors that you can use in graphics. Use the colors() function to get a complete list of available names for colors.
Or you can refer the following color chart.
You can specify colors by index, name, hexadecimal, or RGB value. For example col=1, col='white', and col='#FFFFFF' are equivalent.
Different Plot Types
You can change the type of plot that gets drawn by using the type argument.
Here’s a list of all the different types that you can use.
| Value | Description |
| “p” | Points |
| “l” | Lines |
| “b” | Both points and lines |
| “c” | The lines part alone of “b” |
| “o” | Both points and lines “overplotted” |
| “h” | Histogram like (or high‐density) vertical lines |
| “s” | Step plot (horizontal first) |
| “S” | Step plot (vertical first) |
| “n” | No plotting |
For example, to create a plot with lines between data points, use type='l'; to draw both lines and points, use type='b'.
A series of graphics showing different types is shown below.
Adding Titles and Axis Labels
You can add your own title and axis labels easily by specifying following arguments.
| Argument | Description |
| main | Main plot title |
| xlab | x-axis label |
| ylab | y-axis label |
The Axes Label Style
By specifying the las (label style) argument, you can change the axes label style. This changes the orientation angle of the labels.
| Value | Description |
| 0 | The default, parallel to the axis |
| 1 | Always horizontal |
| 2 | Perpendicular to the axis |
| 3 | Always vertical |
For example, to change the axis style to have all the axes text horizontal, use las=1
The Box Type
Specify the bty (box type) argument to change the type of box round the plot area.
| Value | Description |
| “o” | (default) Draws a complete rectangle around the plot. |
| “n” | Draws nothing around the plot. |
| “l”, “7”, “c”, “u”, or “]” | Draws a shape around the plot area. |
Add a Grid
The plot() function does not automatically draw a grid. However, it is helpful to the viewer for some plots. Call the grid() function to draw the grid once you call the plot().
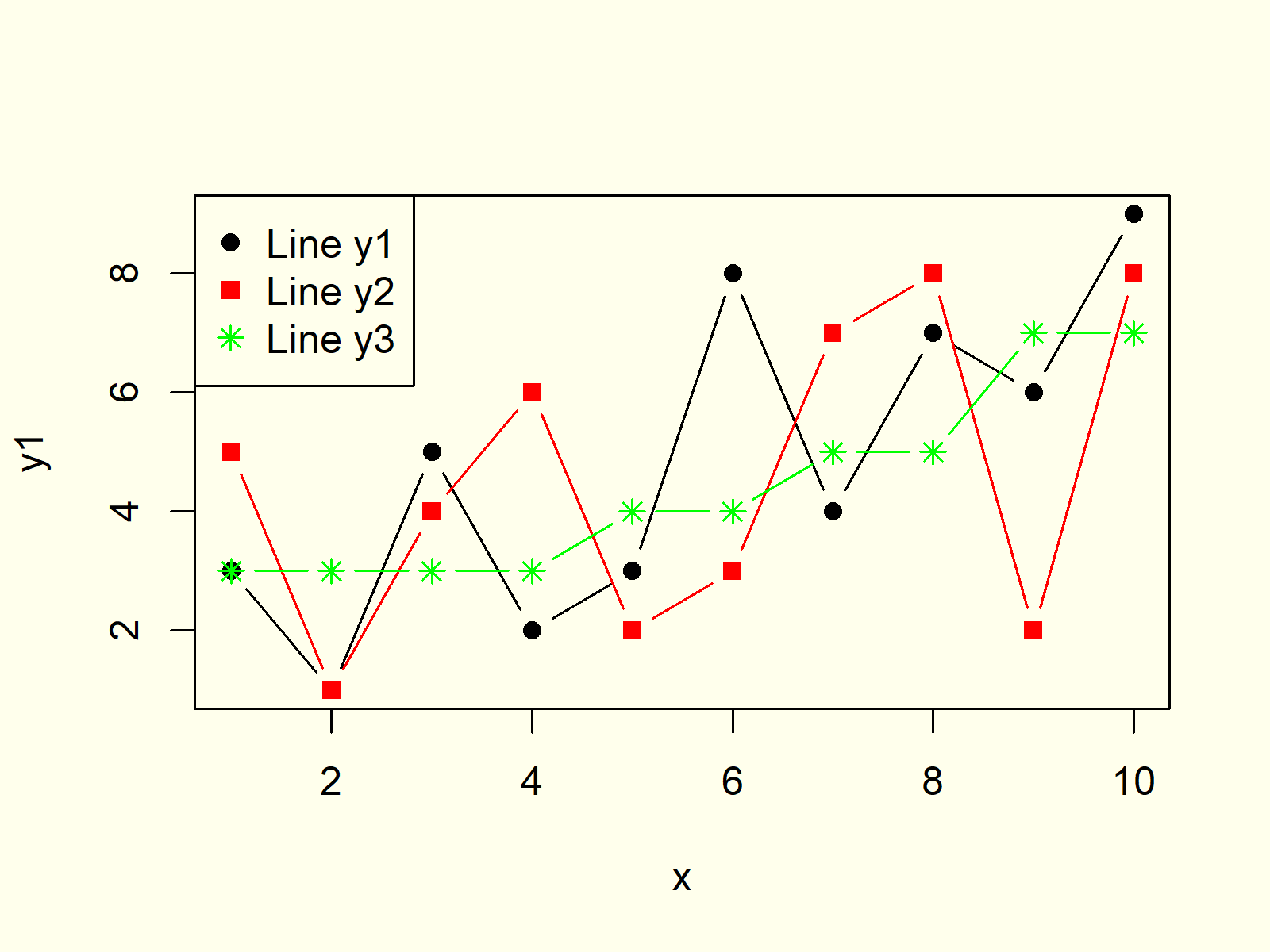
Add a Legend
You can include a legend to your plot – a little box that decodes the graphic for the viewer. Call the legend() function, once you call the plot().
The position of the legend can be specified using the following keywords : “bottomright”, “bottom”, “bottomleft”, “left”, “topleft”, “top”, “topright”, “right” and “center”.
The effect of using each of these keywords is shown below.
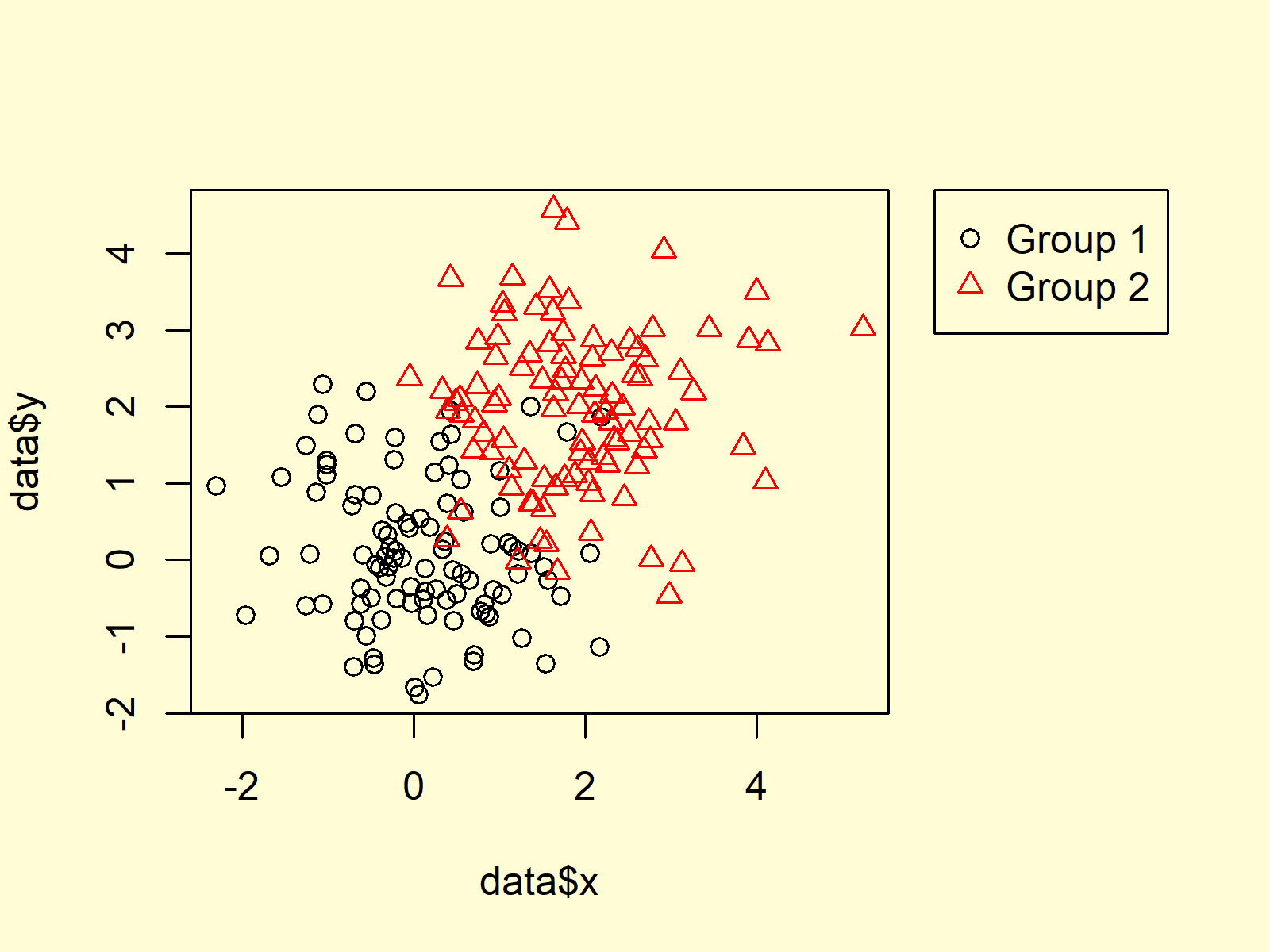
Add Points to a Plot
You can add points to a plot with the points() function.
For example, let’s create a subset of pressure containing temperatures greater than 200 °C and add these points to the plot.
Add Lines to a Plot
You can add lines to a plot in a very similar way to adding points, except that you use the lines() function to achieve this.
You can change the line type using lty argument; and the line width using lwd argument.
Plot Function R
Here’s a list of line types you can use.

Plotting With R
There’s another function called abline() which allows you to draw horizontal, vertical, or sloped lines.
Label Data Points
Use the text() function to add text labels at any position on the plot.
The position of the text is specified by the pos argument. Values of 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively places the text below, to the left of, above and to the right of the specified coordinates.
Set Axis Limits
By default, the plot() function works out the best size and scale of each axis to fit the plotting area. However, you can set the limits of each axis quite easily using xlim and ylim arguments.
Display Multiple Plots on a Single Page
By using the mfrow graphics parameter, you can display multiple plots on the same graphics page.
To use this parameter, you need to pass a two-element vector, specifying the number of rows and columns. Then fill each cell in the matrix by repeatedly calling plot.
For example, mfrow=c(1, 2) creates two side by side plots.
Once your plot is complete, you need to reset your par() options. Otherwise, all your subsequent plots will appear side by side.
Save a Plot to an Image File
Line Plot In R
To save a plot to an image file, you have to do three things in sequence:
- Call a function to open a new graphics file, such as
png(),jpg()orpdf(). - Call
plot()to generate the graphics image. - Call
dev.off()to close the graphics file.
myPlot.png
Plot Types R
Remember that the file will be saved to your current working directory, unless you specify an absolute file path.
